How Many Bones Does The Human Body Consist Of

When humans moved into permanent settlements to farm the human skeletal system weakened from the lack of rigorous exercise required for nomadic hunting and gathering.
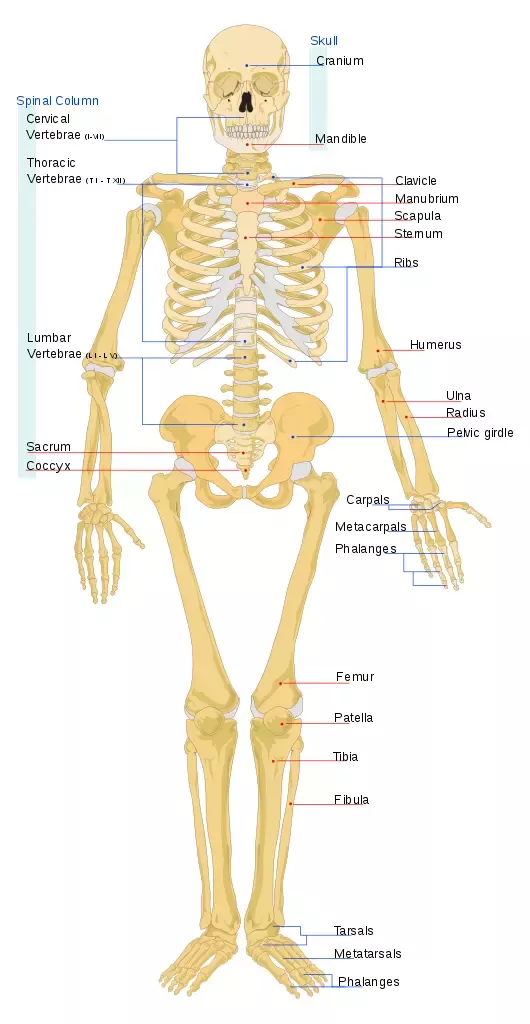
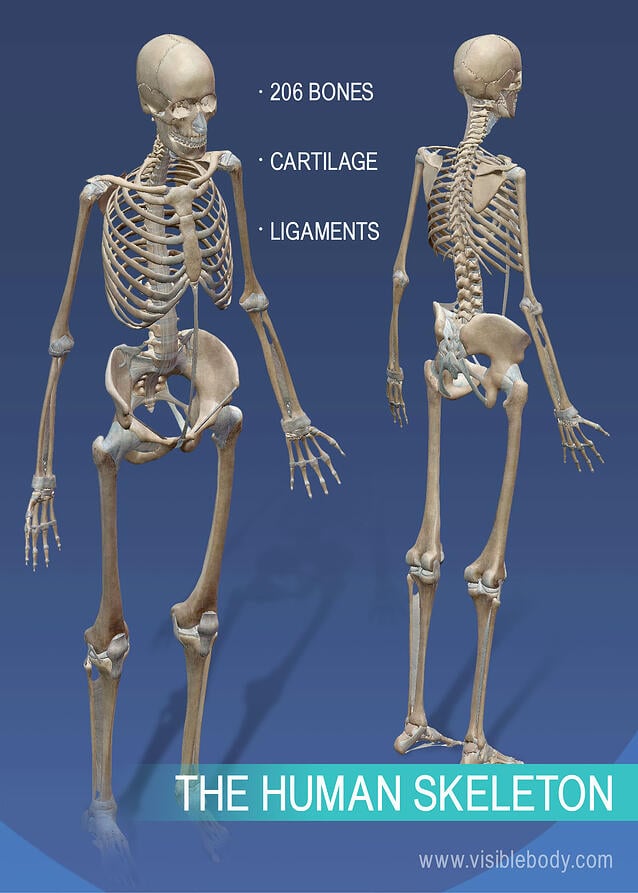
How many bones does the human body consist of. It is composed of around 270 bones at birth this total decreases to around 206 bones by adulthood after some bones get fused together. Babies have more cartilage than bone tissue. The largest bone in the human body is the thighbone or femur and the smallest is the stapes in the middle ear which are just 3 millimeters mm long. The size and shape of a bone varies according to its location in the body.
The pivotal skeleton which includes the bones along with the long hub of the body i e the head and the middle. The human skeleton can be divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The grown up human body contains 206 bones. While the adult human skeletal system includes 206 bones the infantile skeletal system has many more since not all of the bones have fused together yet.
Anatomists separate these into two divisions. The affixed skeleton which incorporates the bones of the members. As a result the adult human skeleton consists of 206 bones. At birth the human body consists of about 300 bones.
As they grow up some of the bones fuse together to form a single bone. The human skeleton of an adult consists of around 206 to 210 bones depending on the counting of sternum which may alternatively be included as the manubrium body of sternum and the xiphoid process it is composed of 270 bones at birth but later decreases to 80 bones in the axial skeleton and 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton.